
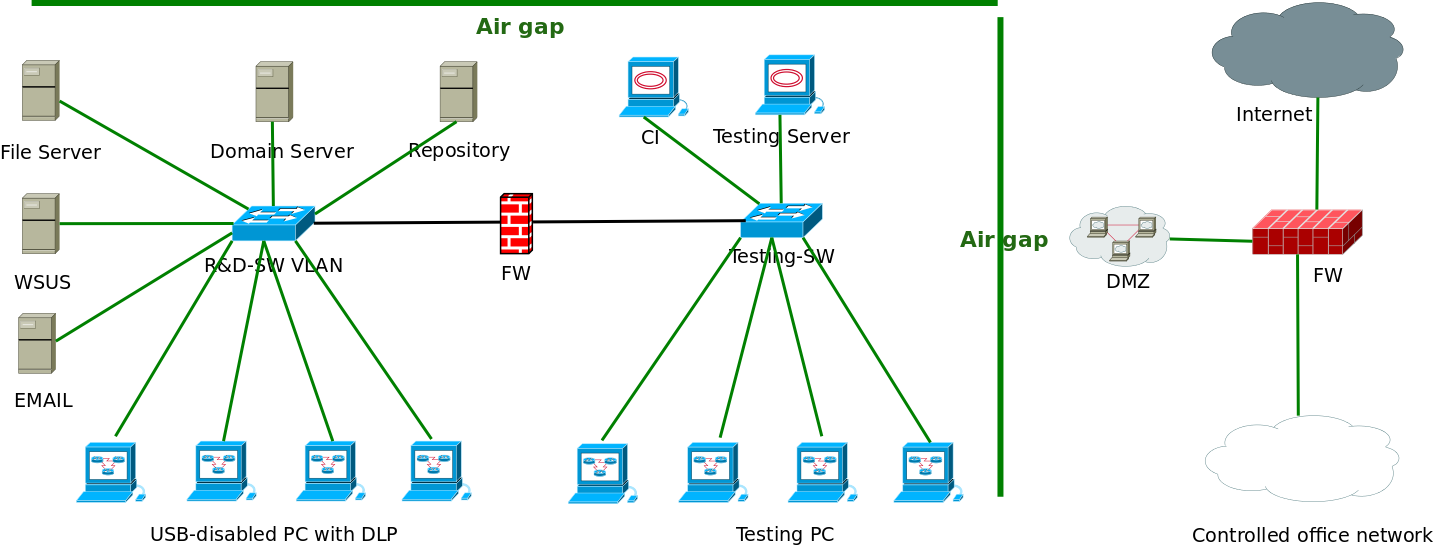
Examples Įxamples of the types of networks or systems that may be air gapped include:

Researchers have also demonstrated the feasibility of data exfiltration using FM frequency signals. The possibility of using acoustic communication has also been demonstrated by researchers.
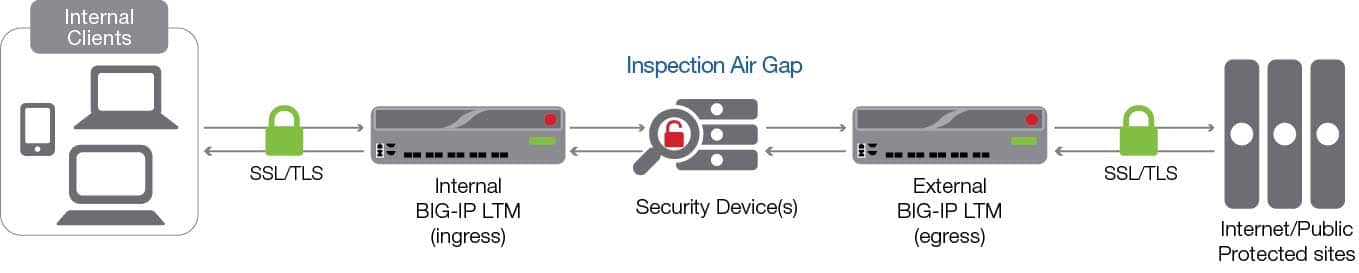
Sophisticated computer viruses for use in cyberwarfare, such as Stuxnet and agent.btz have been designed to infect air-gapped systems by exploiting security holes related to the handling of removable media. That's why another way to transfer data, used in appropriate situations like critical industries, is to use data diodes and electronic airgaps, that assure a physical cut of the network by a specific hardware.
AIR GAPPED NETWORK MANUAL
The downside is that transferring information (from the outside world) to be analyzed by computers on the secure network is extraordinarily labor-intensive, often involving human security analysis of prospective programs or data to be entered onto air-gapped networks and possibly even human manual re-entry of the data following security analysis. The upside to this is that such a network can generally be regarded as a closed system (in terms of information, signals, and emissions security), unable to be accessed from the outside world. This access still has to be carefully controlled since USB drive may have vulnerabilities (see below). One way to transfer data between the outside world and the air-gapped system is to copy data on a removable storage medium such as a removable disk or USB flash drive and physically carry the storage to the other system. The concept represents nearly the maximum protection one network can have from another (save turning the device off). In some cases (for instance industrial critical systems), the policy is different: data can be moved from high-to-low with minimal security measures, but low-to-high requires a high level of procedures to ensure integrity of the industrial safety system. Access policies are often based on the Bell–LaPadula confidentiality model, where data can be moved low-to-high with minimal security measures, while high-to-low requires much more stringent procedures to ensure protection of the data at a higher level of classification. This is also occasionally referred to as red (classified) and black (unclassified). In environments where networks or devices are rated to handle different levels of classified information, the two disconnected devices or networks are referred to as low side and high side, low being unclassified and high referring to classified, or classified at a higher level. That's why some new hardware technologies are also available like unidirectional data diodes or bidirectional diodes (also called electronic airgaps), that physically separate the network and transportation layers and copy and filter the application data.
AIR GAPPED NETWORK FULL
It is easier to control than a direct full network interface, which can be attacked from the exterior insecure system and, if malware infects the secure system, can be used to export secure data. Physical access has to be controlled (man identity and storage media itself). To move data between the outside world and the air-gapped system, it is necessary to write data to a physical medium such as a thumbdrive, and physically move it between computers. This represents a security vulnerability, so air-gapped computers either have their wireless interface controller permanently disabled or physically removed.

AIR GAPPED NETWORK UPDATE
Many computers, even when they are not plugged into a wired network, have a wireless network interface controller ( WiFi) and are connected to nearby wireless networks to access the Internet and update software. An air-gapped computer or network is one that has no network interfaces, either wired or wireless, connected to outside networks.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
